May 23, 2022
Why Establish Contingent Ownership for an Insured Minor
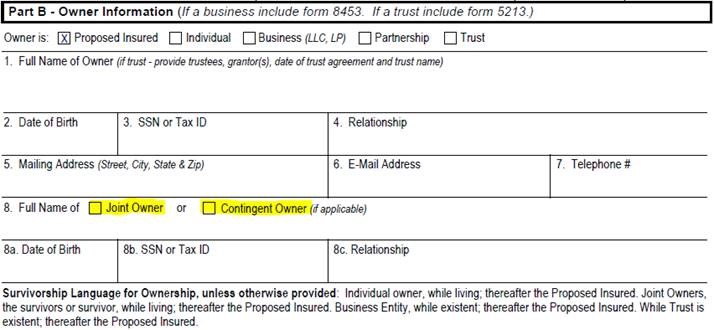
Two ways to structure ownership of the policy so ownership of the policy will not revert to the insured.
On our current life insurance contracts, if an owner of a policy passes away ownership reverts to the insured. If the insured is a minor, this can create additional work as a court appointed legal guardian is required to act on behalf of the child for all dealings with the policy. Additionally, most transactions would require a court order authorizing action requested by the legal guardian.
There are two ways to structure ownership of the policy so ownership of the policy will not revert to the insured. They are…
- Establishing a joint ownership arrangement on a policy or
- Naming a contingent owner for the policy.
Outlined below are requirements needed to establish these arrangements, as well as what this means for the contract.
If a client checks “joint owner” this means the following:
-
- All places where an Applicant/Owner’s signature is requested needs to be signed by both owners (this includes the application and associated forms- like ABR Disclosures etc.)
- This also means that both individuals will have immediate rights to transact on this policy once it is issued/inforce and signed forms on delivery are returned to us.
If a client checks “contingent owner” this means the following:
-
- We will need to collect the contingent owner’s information as shown above, but no signatures are required from the person named as the contingent owner of the policy (compare it to collecting beneficiary information).
- Only when/if the original policy owner passes away do the powers of ownership and ability to transact on the policy transfer to the person named as the contingent owner.